Why does glucose provide us with instant energy?
 |
| Why do we get instant energy from glucose ? |
What is Glucose?
It can help athletes perform at a high level for a longer period of time by delaying fatigue. This means that eating carbohydrates before exercising can help you improve your athletic performance. Glucose tablets can also be used during exercise to raise blood sugar levels.
Your body is powered by glucose. Everything you do consumes energy, from simple tasks like getting out of bed to more strenuous activities like competing in a cross-country race. We get glucose from the food we eat, but you can get a quick boost of glucose by taking quick-acting glucose supplements (typically in chewable tablet form).
Glucose is a type of simple sugar that can be found in a variety of fruits, nuts, and vegetables. It is also the primary source of energy for the body. When we eat, the body converts carbohydrates into glucose before transporting it through the bloodstream.
Blood glucose or blood sugar is the amount of glucose in your bloodstream at any given time. To function, the body requires energy. Your pancreas produces insulin, which aids cell absorption of glucose from the bloodstream, thereby supplying glucose to your brain, organs, and muscles.
Glucose Function and Benefits
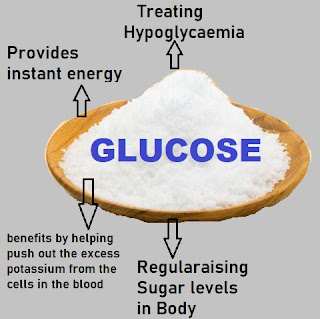 |
| Function and benefits of glucose |
This can occur if we do not eat appropriately, exercise regularly, or take certain medications. Excess insulin can also have an effect on our blood glucose levels. This is why diabetics require insulin shots since they are unable to control the amount of insulin they make.
Sugar and physical activity; the significance of sugar for athletes: Muscle glycogen, the body's most common form of stored glucose, and blood glucose are the primary energy substrates for muscle contraction during exercise. Sucrose is an excellent substance for athletes to consume because it contains both glucose and fructose. As a result, athletes must carefully monitor their diet in order to maintain and increase muscle glycogen deposits, which are a major limiting factor in prolonged exercise performance. Carbohydrate-rich diets are also recommended for endurance and ultra-endurance exercise because they are linked to increased muscle glycogen stores and delayed fatigue onset. Furthermore, high carbohydrate diets and carbohydrate intake before and during exercise have been shown to be beneficial due to higher concentrations of glucose.







0 Comments